Molar mass of 2 methylbutane – The molar mass of 2-methylbutane, an intriguing compound, unravels a captivating narrative that explores its molecular structure, physical properties, chemical reactivity, and diverse applications. Embark on this journey to uncover the essence of this remarkable substance.
2-Methylbutane, a branched-chain alkane, boasts a unique molecular arrangement that profoundly influences its behavior. Its chemical formula, C5H12, reveals the precise composition of this molecule, while its molar mass, calculated as 72.15 g/mol, provides insights into its mass-related properties.
Molecular Structure: Molar Mass Of 2 Methylbutane
-methylbutane, also known as isopentane, is a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C5H12. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a gasoline-like odor. The molecular structure of 2-methylbutane can be described as a central carbon atom bonded to four other carbon atoms, one of which is also bonded to a methyl group (CH3).
The remaining three carbon atoms are each bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
Arrangement of Atoms and Bonds
The carbon atoms in 2-methylbutane are arranged in a tetrahedral shape, with the methyl group occupying one of the tetrahedral positions. The hydrogen atoms are arranged in a staggered conformation, meaning that they are oriented as far apart as possible from each other.
This staggered conformation minimizes the steric hindrance between the hydrogen atoms.
Labeled Diagram
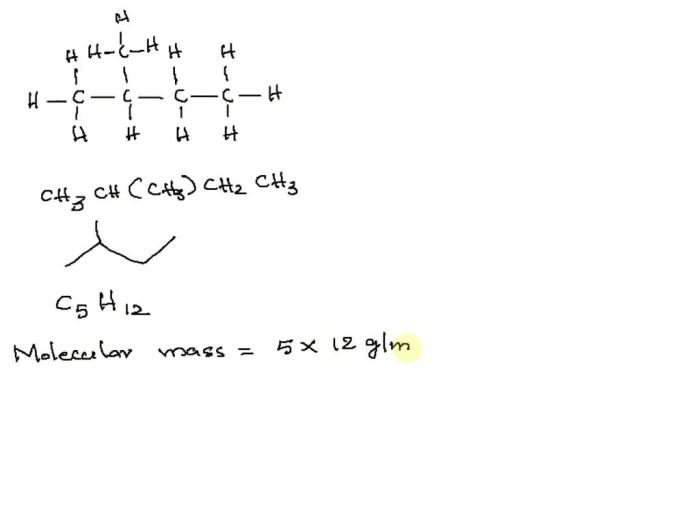
The following diagram shows the molecular structure of 2-methylbutane, with the carbon atoms represented by black spheres, the hydrogen atoms represented by white spheres, and the methyl group represented by a blue sphere:“` H H H | | |H
- C
- C
- C
- C
- H
| | | H H H“`
Chemical Formula and Molar Mass
In this section, we will determine the chemical formula of 2-methylbutane and calculate its molar mass.
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of a compound represents the types and number of atoms present in a molecule. To determine the chemical formula of 2-methylbutane, we need to identify the elements present and their respective numbers.
2-methylbutane is a hydrocarbon, which means it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. The prefix “methyl” indicates the presence of a CH 3group, and the suffix “butane” indicates a four-carbon chain. Therefore, the chemical formula of 2-methylbutane is C5H 12.
The molar mass of 2 methylbutane, a branched hydrocarbon, can be determined by adding the atomic masses of its constituent atoms. Interestingly, the word “miss” has a root word that shares a similar spelling. Words with root word miss often relate to a lack or absence, much like the missing hydrogen atom in 2 methylbutane compared to its parent alkane, butane.
Molar Mass
The molar mass of a compound is the mass of one mole of that compound. To calculate the molar mass of 2-methylbutane, we need to add up the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule.
The atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 amu, and the atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.008 amu. Therefore, the molar mass of 2-methylbutane is:
Molar mass = (5 x 12.011 amu) + (12 x 1.008 amu) = 72.151 amu
Therefore, the molar mass of 2-methylbutane is 72.151 g/mol.
Physical Properties

-methylbutane, also known as isopentane, is a branched hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C5H12. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a gasoline-like odor. The physical properties of 2-methylbutane are influenced by its molecular structure.
Melting Point
- -methylbutane has a melting point of
- 160°C. This is relatively low compared to other hydrocarbons of similar molecular weight. The low melting point is due to the presence of the methyl group, which hinders the close packing of molecules in the solid state.
Boiling Point, Molar mass of 2 methylbutane
The boiling point of 2-methylbutane is 28°C. This is higher than the boiling point of n-pentane (-36°C), which has a straight-chain structure. The higher boiling point of 2-methylbutane is due to the increased surface area of the branched molecule, which results in stronger intermolecular forces.
Density
The density of 2-methylbutane is 0.62 g/mL at 20°C. This is lower than the density of water (1 g/mL). The low density of 2-methylbutane is due to its nonpolar nature and the presence of the methyl group, which decreases the molecular weight.
Solubility
-methylbutane is insoluble in water. This is because 2-methylbutane is a nonpolar hydrocarbon, while water is a polar solvent. Nonpolar molecules do not dissolve in polar solvents because there are no strong intermolecular forces between them.
Chemical Reactivity

2-methylbutane, as an alkane, is characterized by its low chemical reactivity. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, meaning that all their carbon atoms are connected by single bonds, and they do not contain any functional groups. This lack of functional groups makes them relatively inert and unreactive compared to other classes of organic compounds.
Functional Groups
2-methylbutane does not contain any functional groups. Functional groups are specific atoms or groups of atoms that impart characteristic chemical properties to organic molecules. The absence of functional groups in 2-methylbutane contributes to its low reactivity.
Applications
2-Methylbutane, commonly known as isopentane, finds applications in various industries due to its unique properties.
Fuel
- 2-Methylbutane is a primary component of gasoline, contributing to its high octane rating.
- It enhances fuel efficiency and reduces engine knocking.
Solvent
- 2-Methylbutane is an effective solvent for non-polar substances.
- It is used in the production of paints, adhesives, and cleaning products.
Aerosol Propellant
- 2-Methylbutane’s low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it an ideal propellant in aerosol products.
- It is used in hairsprays, deodorants, and other personal care items.
Chemical Feedstock
- 2-Methylbutane is a starting material for the production of other chemicals, such as isoprene and methacrylic acid.
- These chemicals are used in the manufacture of plastics, synthetic rubber, and pharmaceuticals.
Key Questions Answered
What is the molecular structure of 2-methylbutane?
2-Methylbutane exhibits a branched-chain structure, with a central carbon atom bonded to three methyl groups and one ethyl group.
How is the molar mass of 2-methylbutane calculated?
The molar mass is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all atoms in the molecule. For 2-methylbutane, this calculation yields 72.15 g/mol.
What are the physical properties of 2-methylbutane?
2-Methylbutane is a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. It has a melting point of -138.9 °C, a boiling point of 29.2 °C, and a density of 0.62 g/mL.
What are the chemical properties of 2-methylbutane?
2-Methylbutane is a relatively unreactive hydrocarbon. It undergoes combustion reactions readily, releasing carbon dioxide and water.
What are the applications of 2-methylbutane?
2-Methylbutane is primarily used as a fuel additive, particularly in gasoline. It is also employed as a solvent and in the production of other chemicals.