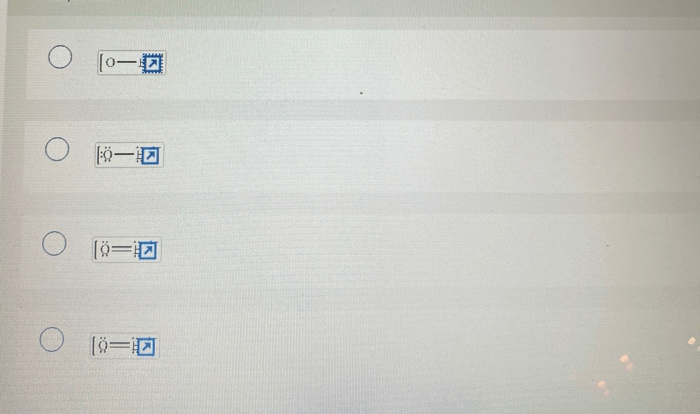
Each pictured Lewis structure is invalid, highlighting the importance of understanding and adhering to the fundamental principles of Lewis structure representation. Lewis structures serve as a crucial tool for visualizing and comprehending the electronic structure and bonding patterns of molecules.
However, inaccuracies in Lewis structure construction can lead to erroneous conclusions and hinder the accurate interpretation of chemical phenomena.
This discussion will delve into the common structural errors, valence electron miscounts, incorrect bonding, formal charge issues, resonance structure misconceptions, octet rule violations, and incomplete structures that render Lewis structures invalid. By examining these errors, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to construct accurate and meaningful Lewis structures, fostering a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and molecular behavior.
Structural Errors: Each Pictured Lewis Structure Is Invalid
Structural errors in Lewis structures arise when the arrangement of atoms and bonds does not accurately represent the molecular geometry. Common errors include:
Incorrect Connectivity
- Atoms may be connected incorrectly, resulting in an invalid molecular structure.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a carbon atom bonded to five other atoms, violating the octet rule.
Missing Bonds
- Essential bonds may be missing, leading to an incomplete Lewis structure.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a carbon atom with only three bonds, neglecting the fourth bond required to satisfy its valence electrons.
Extra Bonds
- Unnecessary or incorrect bonds may be added, creating an invalid Lewis structure.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a carbon atom bonded to six other atoms, exceeding its valence electron capacity.
Valence Electron Miscounts
Valence electrons are crucial in determining the validity of Lewis structures. Errors in counting valence electrons lead to incorrect Lewis structures:
Incorrect Valence Electron Count
- The number of valence electrons assigned to an atom may be incorrect.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a nitrogen atom with only two valence electrons, instead of the correct five.
Unbalanced Valence Electrons
- The total number of valence electrons in the Lewis structure may not match the actual number of valence electrons in the molecule.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a molecule with an odd number of valence electrons, violating the rule of even electron count.
Incorrect Bonding
Lewis structures must adhere to specific rules for single, double, and triple bonds. Errors in bonding patterns can invalidate Lewis structures:
Incorrect Bond Type
- Atoms may be connected by an incorrect bond type, such as a single bond instead of a double bond.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a carbon-oxygen bond as a single bond, when it should be a double bond.
Incorrect Bond Order
- The bond order between atoms may be incorrect, leading to an invalid Lewis structure.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a triple bond between two carbon atoms, which is not possible.
Formal Charge Issues
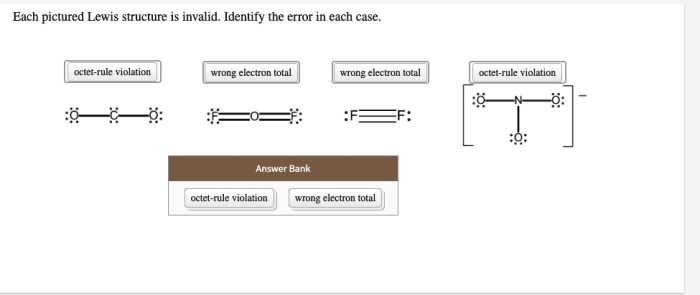
Formal charge analysis helps assess the validity of Lewis structures. Incorrect formal charges indicate structural errors:
Incorrect Formal Charge Calculation
- The formal charges of atoms may be calculated incorrectly.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing an atom with a formal charge that violates the stability guidelines.
Unbalanced Formal Charges
- The sum of formal charges in the Lewis structure may not be equal to the overall charge of the molecule.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a molecule with a formal charge of +1, when it should be neutral.
Resonance Structures
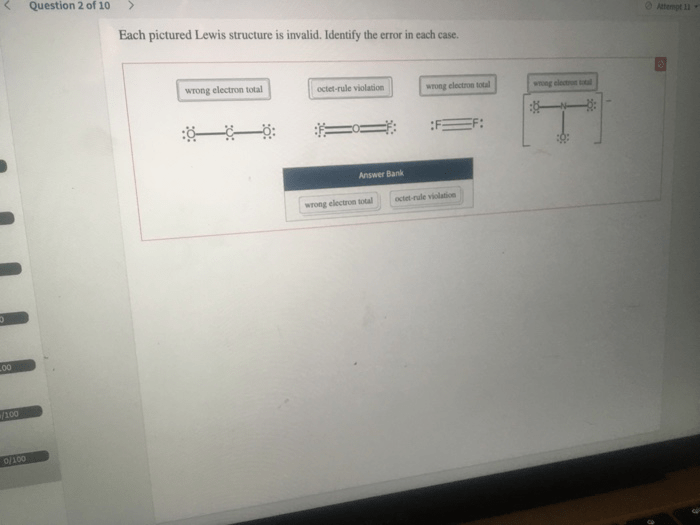
Resonance structures represent the delocalization of electrons in a molecule. Errors in identifying resonance structures can lead to invalid Lewis structures:
Incorrect Resonance Structures, Each pictured lewis structure is invalid
- Invalid resonance structures may be drawn, which do not accurately represent the electron distribution in the molecule.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a resonance structure with an incorrect number of bonds or valence electrons.
Incomplete Resonance Structures
- The set of resonance structures may be incomplete, failing to represent all possible electron distributions.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing only one resonance structure, when there are multiple valid resonance structures.
Octet Rule Violations
The octet rule governs the stability of Lewis structures. Violations of the octet rule can invalidate Lewis structures:
Incomplete Octet
- Atoms may have less than eight valence electrons, violating the octet rule.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a boron atom with only six valence electrons.
Expanded Octet
- Atoms may have more than eight valence electrons, exceeding the octet rule.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a sulfur atom with ten valence electrons.
Exceptions to the Octet Rule
- Some atoms, such as hydrogen and helium, have exceptions to the octet rule and may have fewer or more than eight valence electrons.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a hydrogen atom with only two valence electrons.
Incomplete Structures
Lewis structures must show all atoms and bonds in the molecule. Incomplete structures can lead to invalid Lewis structures:
Missing Atoms
- Essential atoms may be missing from the Lewis structure.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a molecule with only carbon and hydrogen atoms, but missing the oxygen atom that is also present in the molecule.
Missing Bonds
- Essential bonds may be missing from the Lewis structure, leading to an incomplete representation of the molecule.
- Example: A Lewis structure showing a molecule with only single bonds, but neglecting the double bond that is also present in the molecule.
FAQ Overview
What are the most common structural errors found in invalid Lewis structures?
Common structural errors include incorrect placement of atoms, missing or extra bonds, and violations of the octet rule.
How can valence electron miscounts lead to invalid Lewis structures?
Valence electron miscounts occur when the total number of valence electrons assigned to the atoms in a Lewis structure is incorrect, resulting in an unbalanced structure.
What are the rules for single, double, and triple bonds in Lewis structures?
Single bonds consist of one pair of shared electrons, double bonds consist of two pairs of shared electrons, and triple bonds consist of three pairs of shared electrons.
How does formal charge help assess Lewis structure validity?
Formal charge is a tool used to determine the charge distribution within a Lewis structure. Incorrect formal charges indicate errors in bonding or electron distribution.
What is the significance of the octet rule in Lewis structure analysis?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable configuration with eight valence electrons. Violations of the octet rule can lead to invalid Lewis structures.