Ap human geography world regions a closer look – Embarking on an in-depth analysis of AP Human Geography: World Regions A Closer Look, this exploration delves into the multifaceted tapestry of the world’s regions, unraveling their unique characteristics and the intricate interplay between human societies and their environments.
Through a comprehensive examination of physical, cultural, economic, political, and environmental factors, this study unveils the complexities that shape the world’s diverse regions, providing a deeper understanding of the human experience.
Regions and Their Significance
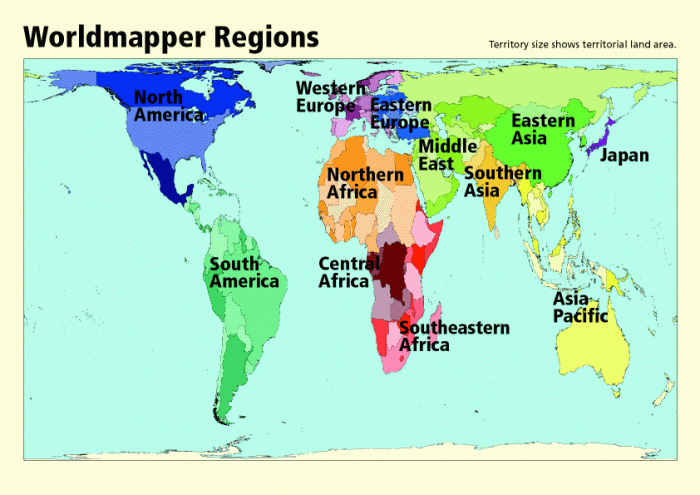
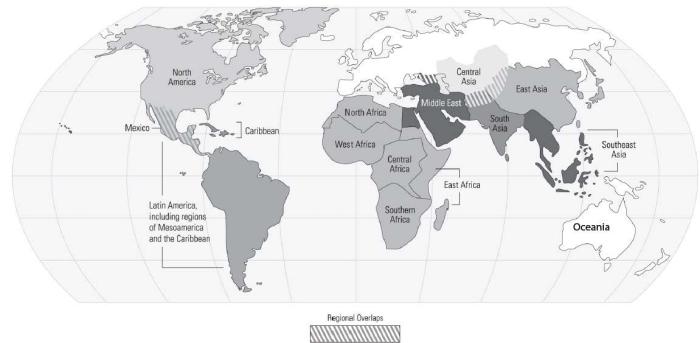
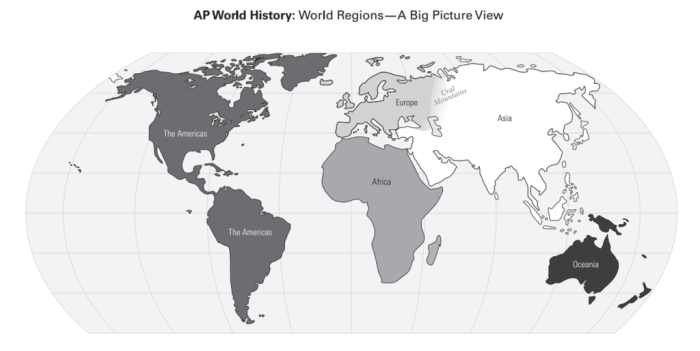
World regions are geographical areas that share similar physical, cultural, economic, political, and environmental characteristics. They are essential for studying human geography because they allow us to understand the complex interactions between humans and their environment within specific contexts.
Regions can be defined using various criteria, such as physical features, climate, cultural practices, political systems, economic activities, or environmental challenges. Major world regions include North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Oceania, each with unique defining characteristics.
Physical Geography of World Regions
The physical geography of world regions refers to their landforms, climate, and vegetation. These factors influence human activities and settlement patterns. For example, mountainous regions tend to have lower population densities due to limited accessibility and harsh conditions, while river valleys and coastal areas are often densely populated due to fertile land and access to water.
- North America:Dominated by the Rocky Mountains, Great Plains, and Great Lakes; temperate climate with regional variations.
- South America:Features the Andes Mountains, Amazon rainforest, and Atacama Desert; tropical climate in the north, temperate in the south.
Cultural Geography of World Regions
The cultural geography of world regions focuses on the dominant languages, religions, and ethnic groups that shape human interactions and the development of societies. Cultural factors influence customs, traditions, values, and beliefs, leading to diverse cultural landscapes.
- Europe:Diverse linguistic and cultural heritage, with major language families including Romance, Germanic, and Slavic; Christian majority with significant Muslim and Jewish minorities.
- Asia:Most populous continent with a wide range of cultures and languages; major religions include Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, and Christianity.
Economic Geography of World Regions
The economic geography of world regions examines economic activities, development patterns, and disparities. Factors such as natural resources, infrastructure, skilled labor, and government policies influence economic growth and development.
- North America:Highly developed economy with a focus on manufacturing, services, and agriculture; major economic centers include New York City and Los Angeles.
- Africa:Developing economy with challenges related to poverty, inequality, and political instability; major economic activities include agriculture, mining, and tourism.
Political Geography of World Regions, Ap human geography world regions a closer look
The political geography of world regions describes the political systems, boundaries, and territorial disputes. Political factors influence regional cooperation and conflict, shaping international relations and global politics.
- Europe:Complex political landscape with a mix of democratic and authoritarian regimes; member states of the European Union have close political and economic ties.
- Middle East:Region of geopolitical significance with ongoing conflicts and territorial disputes; characterized by a mix of monarchies, republics, and authoritarian regimes.
Environmental Geography of World Regions
The environmental geography of world regions examines environmental challenges, human impact on the environment, and strategies for sustainable development. Climate change, pollution, deforestation, and resource depletion are major concerns facing different regions.
- Arctic:Vulnerable to climate change with melting ice caps and thawing permafrost; home to unique ecosystems and indigenous communities.
- Antarctica:Pristine and protected continent; scientific research and environmental conservation are key priorities.
Key Questions Answered: Ap Human Geography World Regions A Closer Look
What is the significance of studying world regions in human geography?
Understanding world regions allows us to grasp the diverse physical, cultural, economic, political, and environmental characteristics that shape human societies and their interactions.
How do physical features influence human activities and settlement patterns?
Physical features such as landforms, climate, and vegetation can influence the availability of resources, transportation routes, and agricultural practices, thereby shaping human settlement patterns and economic activities.
What are the key cultural factors that shape human interactions and societies?
Cultural factors such as language, religion, ethnicity, and values play a crucial role in shaping communication, social norms, and the development of societies.
How do economic disparities between regions arise and what factors contribute to them?
Economic disparities can arise due to differences in resource availability, infrastructure development, access to education and technology, and government policies.
What are the major environmental challenges facing different world regions and what strategies can be employed to address them?
Environmental challenges vary across regions and include issues such as climate change, water scarcity, deforestation, and pollution. Sustainable development strategies, environmental protection policies, and international cooperation are crucial in addressing these challenges.