Embarking on an exploration of art-labeling activity lipids- structure of phospholipids, we delve into a realm where art and science harmoniously intertwine. Art-labeling activities, as we shall discover, possess an extraordinary capacity to ignite student engagement and foster a profound understanding of the intricate world of phospholipids.
Phospholipids, the fundamental building blocks of cell membranes, play a pivotal role in the preservation and texture of artworks. Their structure, meticulously dissected in this discourse, reveals the remarkable interplay of hydrophilic and hydrophobic components that endow them with unique properties.
Moreover, we shall unravel the fascinating role of lipids in diverse art forms, from the vibrant hues of oil paintings to the enduring resilience of sculptures.
Introduction to Art-Labeling Activity
Art-labeling activities are a valuable tool for enhancing student engagement and learning. By labeling and analyzing artwork, students develop their observation skills, critical thinking abilities, and understanding of the subject matter.
Structure of Phospholipids
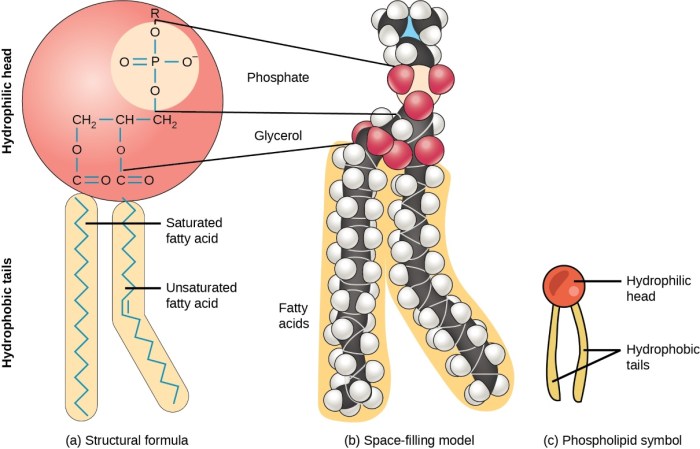
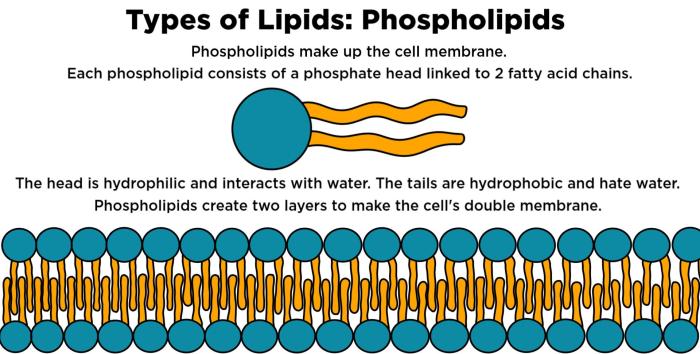
Phospholipids are a type of lipid molecule that are essential for the structure and function of cell membranes. They consist of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate group.
| Component | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol backbone | Three-carbon alcohol | Provides a framework for the molecule |
| Fatty acid tails | Long hydrocarbon chains | Form the hydrophobic core of the membrane |
| Phosphate group | Negatively charged head group | Forms the hydrophilic exterior of the membrane |
Lipids in Art
Lipids play a significant role in various art forms. In oil paintings, lipids are the primary component of the paint, providing texture and color. In sculptures, lipids are used as binders to hold materials together. In textiles, lipids are used to create dyes and waterproofing agents.
- Oil paintings: Lipids in oil paints contribute to the thick, impasto texture and rich colors.
- Sculptures: Lipids in wax sculptures provide a durable and malleable medium for creating intricate forms.
- Textiles: Lipids in dyes enhance colorfastness and protect fabrics from fading.
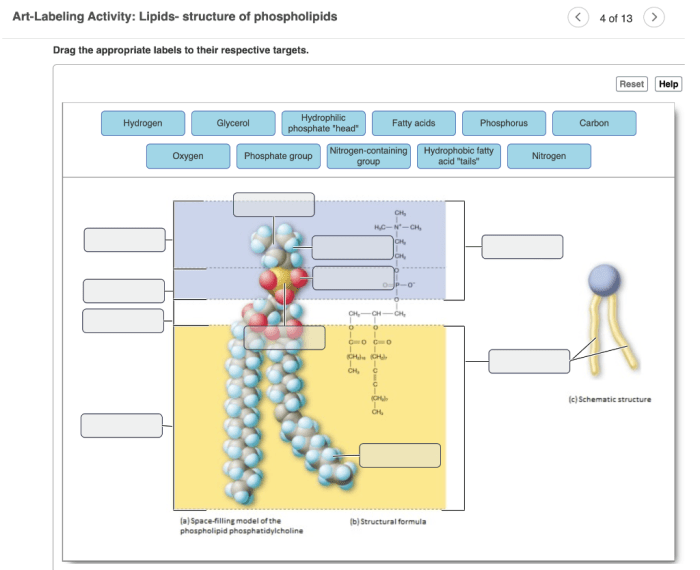
Art-Labeling Activity: Lipids: Art-labeling Activity Lipids- Structure Of Phospholipids
Design an art-labeling activity that focuses on lipids in art. Provide students with instructions on how to identify and label different types of lipids in artworks. Include a variety of artwork examples for students to analyze.
- Identify oil paintings, wax sculptures, and dyed textiles that showcase the use of lipids.
- Provide students with a list of lipid types and their functions in art.
- Guide students in labeling specific areas of the artworks where lipids are present.
Assessment and Discussion
Assess student learning through their ability to identify and label lipids in artwork. Facilitate a class discussion on the role of lipids in art and the importance of art-labeling activities.
- Assessment:Evaluate student responses to the art-labeling activity.
- Discussion points:
- The significance of lipids in preserving and enhancing artwork
- The value of art-labeling activities in promoting observation and critical thinking
- The interdisciplinary nature of art and science
Question & Answer Hub
What are the primary benefits of art-labeling activities?
Art-labeling activities offer a multitude of benefits, including enhanced student engagement, improved comprehension, and the development of critical thinking skills.
How do lipids contribute to the preservation of artwork?
Lipids act as a protective barrier against environmental factors such as moisture and oxidation, safeguarding the integrity of artworks over time.