Quiz Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells embarks on a journey into the captivating realm of cellular biology. Delving into the intricacies of these two distinct cell types, this comprehensive quiz unravels their fundamental differences, shedding light on the very essence of life.
As we embark on this quest for knowledge, we will explore the diverse structures, metabolic processes, evolutionary histories, and ecological roles that set prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells apart, providing a deeper understanding of the building blocks of life.
Cell Structure and Organization
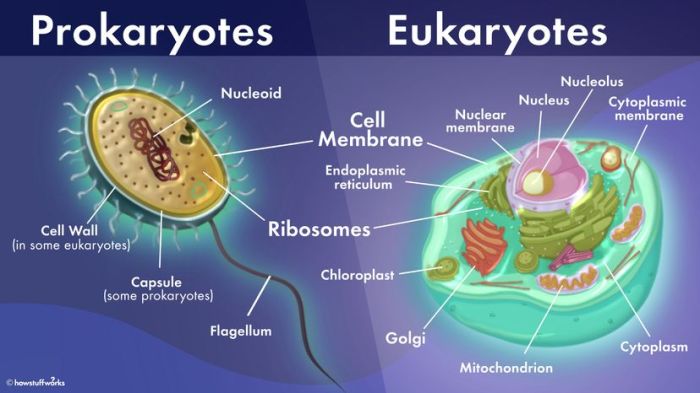
Cells are the fundamental unit of life and come in two basic types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Basic Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
The basic structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is summarized in the table below:
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Nuclear Membrane | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Absent (in most cases) | Present (in plant cells) |
| Cell Wall | Present | Present (in plant cells) |
| Cell Membrane | Present | Present |
Diagram Organelles in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
The diagram below illustrates the different organelles found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
[Diagram di sini]
Cell Function and Metabolism
Metabolic Processes in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells use different metabolic processes to obtain energy and carry out cellular functions. Prokaryotic cells typically rely on fermentation or anaerobic respiration, while eukaryotic cells primarily use aerobic respiration.
Energy Sources and Waste Products of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
The energy sources and waste products of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are summarized in the table below:
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Organic molecules, inorganic molecules | Organic molecules |
| Waste Product | Carbon dioxide, water, organic acids | Carbon dioxide, water |
Cell Division in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, Quiz prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells also differ in their methods of cell division. Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission, a simple process that results in two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis and meiosis, more complex processes that result in genetically diverse daughter cells.
Evolution of Cells
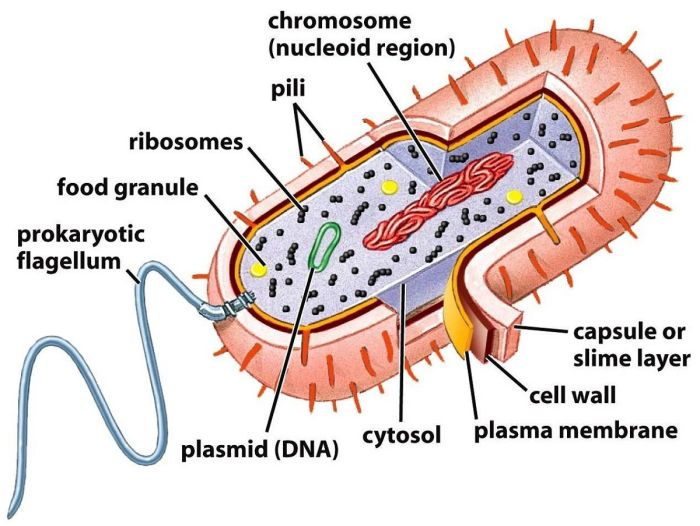
Theories Regarding the Evolution of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
The evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is a complex and debated topic. One of the leading theories is the endosymbiotic theory, which proposes that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between a prokaryotic cell and a smaller, photosynthetic cell.
Evidence to Support the Endosymbiotic Theory
There is considerable evidence to support the endosymbiotic theory, including:
- The presence of endosymbiotic bacteria in modern eukaryotic cells
- The similarity of the DNA of mitochondria and chloroplasts to the DNA of free-living bacteria
- The double membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts, which suggest that they were once independent cells
Timeline of Major Events in the Evolution of Cells
The following timeline illustrates the major events in the evolution of cells:
- 3.5 billion years ago: Origin of life
- 2.7 billion years ago: Evolution of photosynthesis
- 1.5 billion years ago: Evolution of eukaryotes
- 540 million years ago: Evolution of multicellular organisms
Cell Diversity: Quiz Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells
Types of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
There are a wide variety of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea. Some of the most common types of eukaryotic cells include animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
Characteristics of Different Types of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
The characteristics of different types of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are summarized in the table below:
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 0.1-5 μm | 10-100 μm |
| Shape | Spherical, rod-shaped, spiral | Variable |
| Number of Cells | Unicellular | Unicellular or multicellular |
| Reproduction | Binary fission | Mitosis or meiosis |
| Metabolism | Fermentation or anaerobic respiration | Aerobic respiration |
Ecological Roles of Different Types of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells play a variety of important ecological roles. Prokaryotic cells are essential for nutrient cycling and decomposition. Eukaryotic cells are essential for photosynthesis, the production of oxygen, and the formation of food chains.
User Queries
What is the primary structural difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess these structures.
How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in their energy sources?
Prokaryotic cells can utilize a wider range of energy sources than eukaryotic cells, including inorganic compounds and sunlight.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between prokaryotic cells.