Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of pollination flower to fruit gizmo answers, where we unravel the intricate mechanisms of nature’s reproductive dance. From the vibrant petals that beckon pollinators to the remarkable transformation of flowers into fruits, this exploration unveils the wonders of plant reproduction.
Delve into the fascinating world of pollination, where insects, birds, and wind play crucial roles in facilitating the fertilization of flowers. Discover how flower structure and adaptations influence pollinator attraction, ensuring the continuation of plant species.
Pollination Process
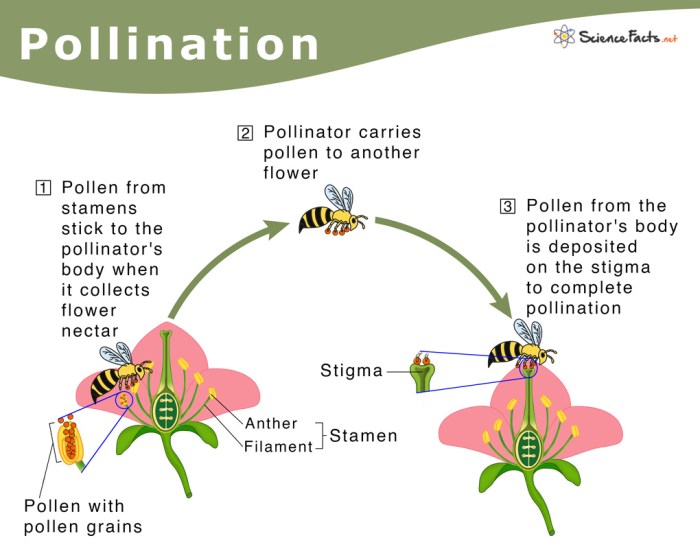
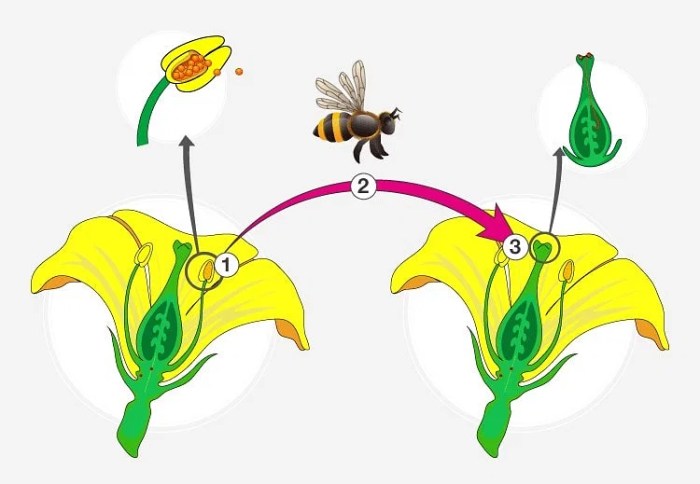
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. This process is crucial for plant reproduction and fruit development. The steps involved in pollination include:
- Pollen production: The anthers of a flower produce pollen grains, which contain the male gametes.
- Pollen dispersal: Pollen grains are dispersed by various agents, such as insects, birds, wind, or water.
- Pollen landing: Pollen grains land on the stigma of a compatible flower, which is the female reproductive structure.
- Pollen tube growth: A pollen tube grows from the pollen grain, down the style, towards the ovary.
- Fertilization: The pollen tube delivers the male gametes to the ovules in the ovary, resulting in fertilization.
Role of Different Pollinators
Various organisms play vital roles as pollinators, including:
- Insects: Bees, butterflies, and moths are common insect pollinators that transfer pollen as they collect nectar from flowers.
- Birds: Hummingbirds and sunbirds are examples of avian pollinators that feed on nectar and inadvertently transfer pollen.
- Wind: Wind-pollinated flowers have light, dry pollen grains that can be easily carried by wind currents.
Specific examples of plant species and their pollinators include:
- Roses: Pollinated by bees
- Apples: Pollinated by bees and other insects
- Corn: Wind-pollinated
Flower Structure and Pollination
Parts of a Flower
The different parts of a flower involved in pollination include:
- Petals: Colorful and fragrant petals attract pollinators.
- Sepals: Leaf-like structures that protect the flower bud.
- Anthers: Male reproductive structures that produce pollen.
- Stigma: Female reproductive structure that receives pollen grains.
- Style: A stalk that connects the stigma to the ovary.
- Ovary: Contains the ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization.
Attracting Pollinators
Flowers have evolved various adaptations to attract pollinators:
- Color: Brightly colored flowers are easily visible to pollinators.
- Shape: Flowers with specific shapes provide easy access to pollinators.
- Scent: Flowers release fragrances that attract pollinators.
Preventing Self-Pollination
Some plants have adaptations to prevent self-pollination, such as:
- Dichogamy: Flowers have male and female parts that mature at different times.
- Self-incompatibility: Pollen grains are unable to fertilize ovules from the same flower.
- Structural barriers: Flowers have physical barriers that prevent self-pollination.
Fruit Development after Pollination
After successful pollination, the ovary of the flower develops into a fruit. This process involves:
- Ovule development: The ovules in the ovary develop into seeds.
- Fruit wall development: The ovary wall thickens and develops into the fruit.
- Hormonal regulation: Hormones, such as auxin and gibberellin, play crucial roles in fruit growth and ripening.
Types of Fruits
Fruits vary in their characteristics and can be classified into different types, including:
- Fleshy fruits: Have a soft and juicy flesh, such as apples, oranges, and berries.
- Dry fruits: Have a hard and dry outer covering, such as nuts, legumes, and grains.
- Aggregate fruits: Develop from multiple ovaries of a single flower, such as strawberries and raspberries.
Gizmo Pollination Simulation
Features and Functions, Pollination flower to fruit gizmo answers
A pollination gizmo is a virtual simulation that allows students to explore the process of pollination.
Its features include:
- Interactive flower models
- Different pollinator types
- Control over pollination parameters
Functions of a pollination gizmo include:
- Visualizing the steps of pollination
- Experimenting with different variables
- Assessing the impact of pollination on fruit development
Educational Uses
Pollination gizmos can be used for educational purposes, such as:
- Teaching the concepts of pollination
- Demonstrating the role of pollinators
- Investigating the factors that affect pollination success
Pollination in Different Ecosystems
Pollination plays a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem health:
- Food production: Pollination is essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, and other crops.
- Plant reproduction: Pollination ensures the successful reproduction of flowering plants.
- Habitat provision: Pollinators provide food and shelter for other organisms.
Impact of Human Activities
Human activities can negatively impact pollination, including:
- Habitat loss: Destruction of natural habitats reduces pollinator populations.
- Pesticide use: Pesticides can harm pollinators.
- Climate change: Changes in climate can disrupt pollination patterns.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts to protect pollinators include:
- Habitat restoration: Creating and restoring pollinator-friendly habitats.
- Reduced pesticide use: Adopting integrated pest management practices to minimize harm to pollinators.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of pollinators and promoting their conservation.
Query Resolution: Pollination Flower To Fruit Gizmo Answers
What is the role of pollinators in the pollination process?
Pollinators, such as insects, birds, and wind, play a crucial role in transferring pollen grains from the male anther to the female stigma of a flower, facilitating fertilization and seed production.
How does flower structure influence pollinator attraction?
Flowers have evolved diverse structures and adaptations, such as vibrant colors, distinct shapes, and alluring scents, to attract specific pollinators. These adaptations ensure efficient pollen transfer and successful reproduction.
What is the significance of pollination in ecosystems?
Pollination is essential for the reproduction of flowering plants, which form the foundation of many food chains and provide sustenance for countless animal species. Pollination also contributes to genetic diversity and the maintenance of healthy ecosystems.