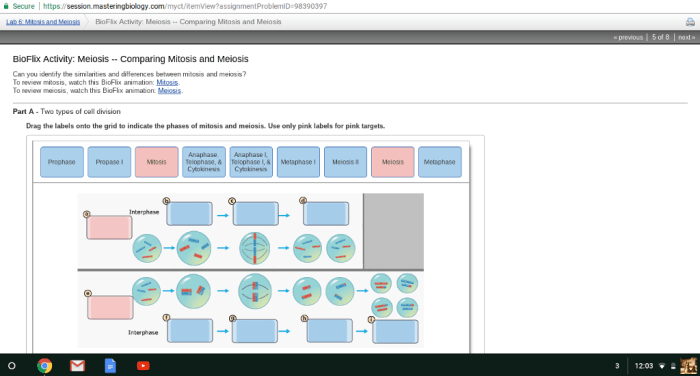
Bioflix activity meiosis comparing mitosis and meiosis – Delve into the realm of cellular division with BioFlix’s captivating activity, which unravels the intricate dance between meiosis and mitosis. This comprehensive exploration illuminates the fundamental differences between these two vital processes, shedding light on their significance in genetics, reproduction, and beyond.
Throughout this engaging journey, we will delve into the distinct stages of meiosis I and II, contrasting them with the familiar phases of mitosis. We will explore the role of chromosomes in these processes and uncover how meiosis contributes to genetic variation, a cornerstone of evolution.
Understanding Meiosis and Mitosis

Meiosisand mitosisare two distinct types of cell division that play crucial roles in the life cycle of all organisms. Meiosis is the process of cell division that produces gametes (sex cells), while mitosis is the process of cell division that produces somatic cells (body cells).
Key differences between meiosis and mitosisinclude the number of daughter cells produced, the number of chromosome replications, and the genetic variation in the daughter cells.
Stages of Meiosis and Mitosis
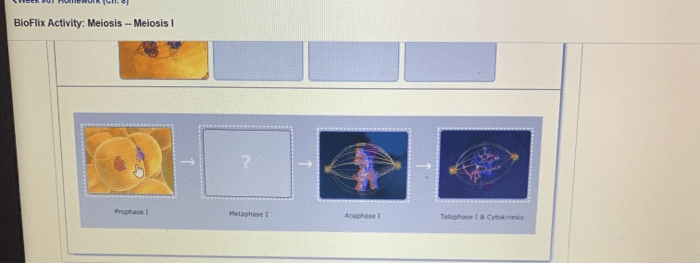
Meiosisconsists of two divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, each of which is further divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This results in genetic recombination and increased genetic variation in the daughter cells.
Mitosis, on the other hand, consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. During mitosis, the chromosomes are duplicated and separated into two daughter cells, each of which receives an identical set of chromosomes. Mitosis is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair.
The following table summarizes the stages of meiosis and mitosis:
| Stage | Meiosis | Mitosis |
|---|---|---|
| Prophase I | Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material | Chromosomes condense and become visible |
| Metaphase I | Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell | Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell |
| Anaphase I | Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell | Chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell |
| Telophase I | Two daughter cells are formed, each with a haploid number of chromosomes | Two daughter cells are formed, each with a diploid number of chromosomes |
| Prophase II | Chromosomes condense and become visible | N/A |
| Metaphase II | Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell | N/A |
| Anaphase II | Chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell | N/A |
| Telophase II | Four daughter cells are formed, each with a haploid number of chromosomes | N/A |
| Cytokinesis | The cytoplasm divides, separating the four daughter cells | The cytoplasm divides, separating the two daughter cells |
Chromosomes and Genetic Variation: Bioflix Activity Meiosis Comparing Mitosis And Meiosis
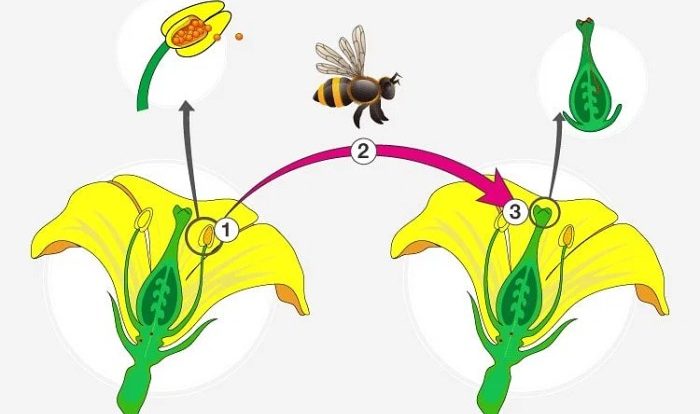
Chromosomesare thread-like structures in the nucleus of a cell that contain genetic material. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, resulting in genetic recombination and increased genetic variation in the daughter cells. This genetic variation is essential for the survival of a species, as it allows for adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Mitosis, on the other hand, produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair, as it ensures that all cells in the body have the same genetic information.
Significance of Meiosis and Mitosis

Meiosisis essential for sexual reproduction. It produces gametes (sex cells), which contain half the number of chromosomes as somatic cells. When two gametes fuse during fertilization, they create a zygote with a complete set of chromosomes. This process ensures that each new individual has a unique combination of genetic material.
Mitosisis essential for growth, development, and tissue repair. It produces somatic cells, which contain the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This ensures that all cells in the body have the same genetic information, which is necessary for proper functioning.
Meiosis and mitosisare also used in biotechnology and medicine. For example, meiosis is used in the production of genetically modified crops, while mitosis is used in the production of stem cells.
Meiosis and Mitosis in Different Organisms
Meiosis and mitosisoccur in all organisms, but there are some variations in the processes across different groups. For example, in some plants, meiosis occurs in the anthers of the flowers, while in some animals, it occurs in the testes or ovaries.
The following table summarizes the key differences in meiosis and mitosis across different organisms:
| Organism | Meiosis | Mitosis |
|---|---|---|
| Plants | Occurs in the anthers of the flowers | Occurs in the root tips and other growing regions |
| Animals | Occurs in the testes or ovaries | Occurs in all cells of the body |
| Fungi | Occurs in the hyphae | Occurs in the mycelium |
Disorders Related to Meiosis and Mitosis
Errors in meiosiscan lead to a number of genetic disorders, including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. These disorders are caused by an abnormal number of chromosomes in the cells.
Errors in mitosiscan lead to a number of diseases, including cancer. Cancer is caused by the uncontrolled growth of cells, which can be caused by errors in mitosis that lead to the formation of cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes.
Genetic counselingcan help individuals and families understand the risks of genetic disorders and make informed decisions about their reproductive choices.
FAQ Explained
What is the primary distinction between meiosis and mitosis?
Meiosis results in the production of gametes (sex cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic variation?
During meiosis, genetic recombination occurs, leading to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process creates new combinations of alleles, increasing genetic diversity within a population.
What are some examples of disorders associated with errors in meiosis or mitosis?
Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and certain types of cancer are examples of disorders that can arise from errors during meiosis or mitosis.