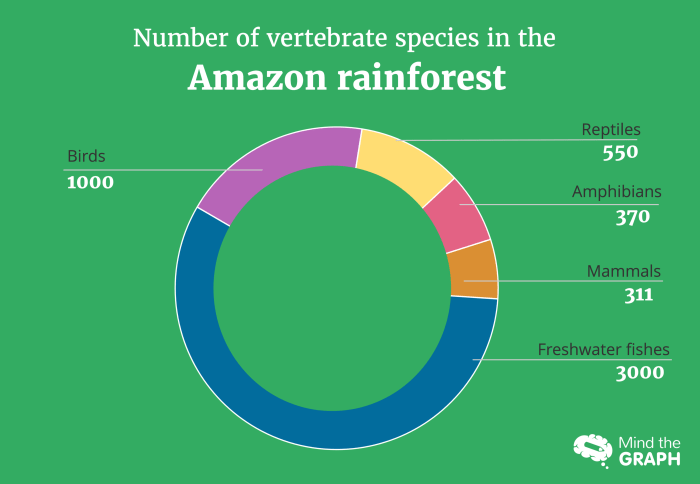
The sustainable use of rainforest resources is exemplified by an intricate interplay between conservation and economic development, where the preservation of natural treasures goes hand in hand with the empowerment of local communities. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of this delicate balance, exploring the techniques, challenges, and successes of sustainable resource management in rainforest ecosystems.
Striking a harmonious balance between the preservation of rainforest resources and the economic well-being of local communities is a formidable task, yet one that is essential for the long-term sustainability of both. This article examines the intricacies of this balancing act, showcasing successful initiatives that have integrated sustainable resource use with local economic growth.
1. Understanding Sustainable Rainforest Resource Use: The Sustainable Use Of Rainforest Resources Is Exemplified By
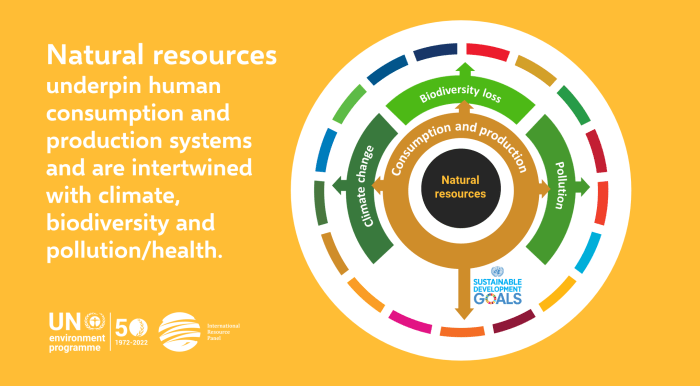
Sustainable resource use in the context of rainforests entails utilizing rainforest resources in a manner that ensures their long-term preservation and the well-being of both present and future generations. This involves adopting practices that minimize environmental impact, preserve biodiversity, and support the livelihoods of local communities dependent on rainforest resources.
Examples of sustainable practices include selective logging, which involves harvesting only mature trees while leaving younger trees to grow, and agroforestry, which integrates trees into agricultural systems to provide multiple benefits, such as food, timber, and soil conservation.
2. Methods for Sustainable Resource Extraction, The sustainable use of rainforest resources is exemplified by
Various techniques are employed for sustainable logging, mining, and harvesting of non-timber forest products in rainforests. These include:
- Reduced-impact logging: Utilizes techniques to minimize damage to the forest ecosystem, such as directional felling, reduced skidding trails, and buffer zones around sensitive areas.
- Community-based forest management: Involves local communities in forest management and decision-making, empowering them to protect their traditional lands and ensure sustainable resource use.
- Certification schemes: Provide independent verification of sustainable forest management practices, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and the Rainforest Alliance.
3. Balancing Conservation and Economic Development
Balancing the need for economic development with rainforest conservation presents challenges, but also opportunities. Sustainable resource use can contribute to local economic growth by providing employment, generating income, and supporting traditional livelihoods.
Case studies of successful initiatives include:
- Payments for ecosystem services: Compensating local communities for preserving rainforest resources, such as carbon sequestration and watershed protection.
- Ecotourism: Generating revenue from responsible tourism that showcases the beauty and biodiversity of rainforests.
4. Role of Indigenous Knowledge and Traditional Practices
Incorporating indigenous knowledge and traditional practices is crucial for sustainable rainforest resource management. Indigenous communities possess a wealth of knowledge about rainforest ecosystems and have developed sustainable practices over generations.
Their involvement can contribute to:
- Conservation of biodiversity: Traditional practices often emphasize the preservation of keystone species and habitats.
- Sustainable resource use: Indigenous communities can share knowledge about sustainable harvesting techniques and medicinal plants.
- Cultural preservation: Traditional practices are an integral part of indigenous cultures and their continued use contributes to cultural heritage.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation of Sustainable Practices
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of sustainable resource use practices is essential to ensure their continued success. This involves:
- Establishing indicators: Identifying specific metrics to measure progress towards sustainability goals, such as forest cover, biodiversity, and socio-economic indicators.
- Regular monitoring: Collecting data on indicators over time to track changes and identify any issues.
- Adaptive management: Using monitoring results to adjust practices and policies as needed to improve effectiveness.
Clarifying Questions
What are the key principles of sustainable rainforest resource use?
Sustainable rainforest resource use involves practices that minimize environmental impact, preserve biodiversity, and support the long-term well-being of local communities.
How can sustainable logging be implemented in rainforests?
Sustainable logging involves selective harvesting techniques, reduced-impact logging methods, and reforestation efforts to ensure the long-term health of rainforest ecosystems.
What role do indigenous communities play in sustainable rainforest management?
Indigenous communities possess valuable knowledge and traditional practices that can contribute to sustainable rainforest management, including agroforestry, wildlife conservation, and sustainable harvesting techniques.