Amoeba sisters video recap ecological relationships answer key – Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Ecological Relationships Answer Key provides a comprehensive review of the ecological relationships explored in the Amoeba Sisters video. This guide will delve into the fundamental concepts of predator-prey dynamics, competition, mutualism, food webs, energy flow, resource partitioning, symbiotic relationships, ecological succession, and human impacts on ecosystems.
By unlocking the intricacies of these ecological interactions, we gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Ecological Relationships
The Amoeba Sisters video provides a comprehensive overview of ecological relationships, covering key concepts such as predator-prey interactions, competition, and mutualism. It illustrates these concepts with engaging examples and animations.
Ecological Relationships: Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Ecological Relationships Answer Key
Ecological relationships describe the interactions between organisms within an ecosystem. These relationships can be classified into three main types:
Predator-Prey Relationships
- One organism (predator) hunts and consumes another organism (prey).
- Example: Lions preying on zebras.
Competition
- Organisms compete for limited resources, such as food, water, or territory.
- Example: Grasshoppers competing for food in a meadow.
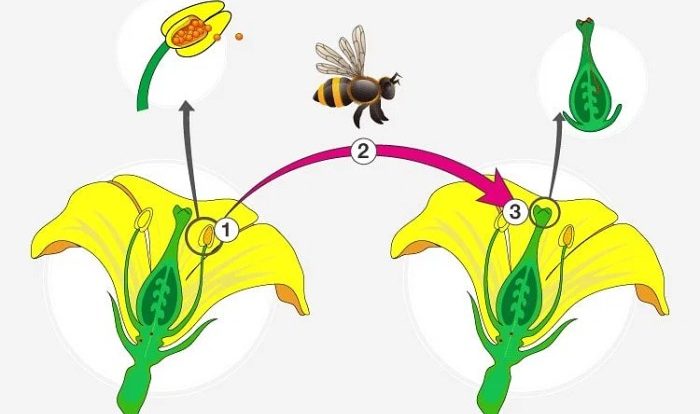
Mutualism
- Both organisms benefit from the interaction.
- Example: Pollination of flowers by bees.
Food Webs and Energy Flow
Food webs depict the interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Energy flows through food webs as organisms consume each other.
Producers
- Organisms that create their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Example: Plants and algae.
Consumers, Amoeba sisters video recap ecological relationships answer key
- Organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms.
- Example: Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
Decomposers
- Organisms that break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the ecosystem.
- Example: Bacteria and fungi.
Competition and Resource Partitioning
Competition occurs when organisms require the same resources. To reduce competition, species may engage in resource partitioning, where they specialize in different niches or use resources at different times.
Example:
- Two species of birds may coexist in the same forest by specializing in different heights of trees.
Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiosis describes close interactions between different species. These relationships can be categorized as:
Mutualism
- Both species benefit from the interaction.
- Example: Cleaner fish and host fish.
Commensalism
- One species benefits while the other is unaffected.
- Example: Barnacles attached to a whale.
Parasitism
- One species (parasite) benefits at the expense of the other (host).
- Example: Tapeworms in the intestines of humans.
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the gradual change in the composition of species within an ecosystem over time. It occurs in stages, from pioneer species to climax communities.
Factors Influencing Succession
- Climate
- Soil conditions
- Disturbances (e.g., fire, hurricanes)
Human Impact on Ecological Relationships
Human activities can significantly impact ecological relationships, both positively and negatively.
Positive Impacts
- Conservation efforts
- Reforestation
Negative Impacts
- Pollution
- Habitat destruction
- Invasive species
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of ecological relationships?
Ecological relationships are crucial for maintaining ecosystem stability, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity. They determine the distribution, abundance, and behavior of species within a community.
How does competition influence species interactions?
Competition occurs when organisms utilize the same limited resources, such as food or habitat. It can lead to niche partitioning, where species evolve to specialize in different resources to reduce competition.
What are the different types of symbiotic relationships?
Symbiotic relationships encompass mutualism (both species benefit), commensalism (one species benefits while the other is unaffected), and parasitism (one species benefits at the expense of the other).